If you’re experiencing pain on the outside of your elbow, it could be tennis elbow. Common symptoms include pain, tenderness, and difficulty gripping or lifting. In this post, we’ll take a close look at these symptoms, as well as diagnosis and treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is caused by repetitive wrist and arm motions that lead to tendon inflammation and pain on the outside of the elbow.
- Common symptoms include elbow pain, reduced grip strength, and movement-induced discomfort, which can hinder daily activities.
- Management typically involves rest, physical therapy, medications, and activity modifications.
Understanding Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a condition where the tendons in the elbow become overloaded, usually due to repetitive motions of the wrist and arm. This overuse can lead to inflammation and tiny tears in the tendons that attach to the outer part of the elbow.
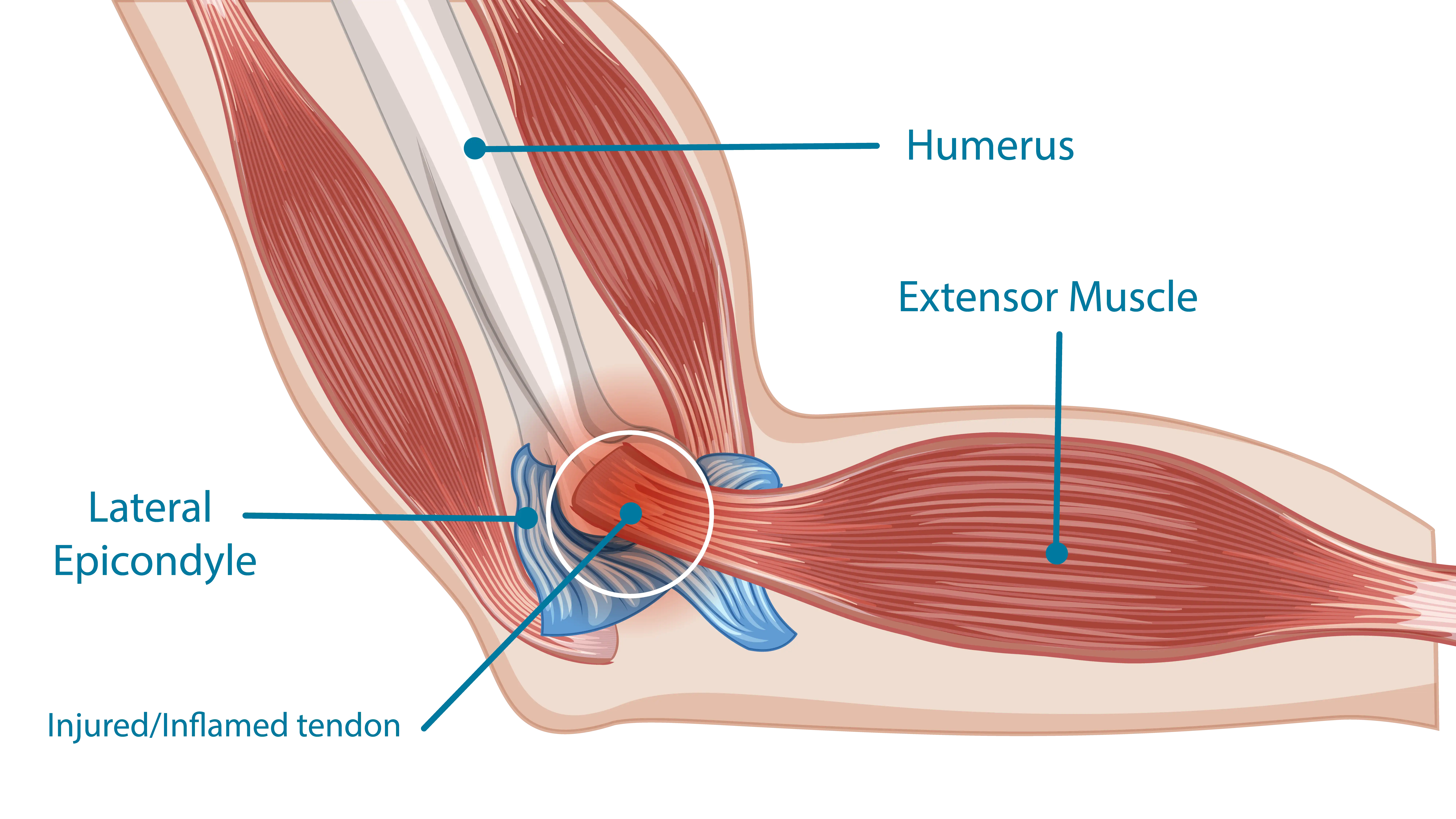
Despite its name, you don’t have to play tennis to develop tennis elbow. It’s common in various activities and professions. Potential triggers include racket sports and performing repetitive tasks such as typing, painting, or using hand tools.
Understanding the causes of tennis elbow can help with early symptom recognition and prevention.
Detailed Symptoms Breakdown
The main symptom of tennis elbow is pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow, but there are several other symptoms to be aware of. These symptoms can vary in intensity. In the following subsections, we’ll explore specific symptoms like pain and tenderness, grip strength reduction, and movement-induced pain.
Pain and Tenderness
One of the hallmark symptoms of tennis elbow is elbow pain that often begins at the outside of the elbow and may radiate down the forearm and into the wrist. This pain may be exacerbated by activities involving lifting, gripping, or twisting. The area may also become tender to the touch, especially when pressed.
Grip Strength Reduction
Tennis elbow can significantly reduce grip strength, making daily tasks more difficult. Pain and forearm weakness may impair your ability to shake hands, open jars, or carry groceries. If you notice a decline in your ability to hold or lift objects, it might be indicative of tennis elbow or another condition.
Movement-Induced Pain
Repetitive movements of the arm and wrist can aggravate tennis elbow. Pain may worsen during actions such as bending, stretching, twisting, grasping, or lifting. Repeated strain on the irritated tendon causes this movement-induced pain. Without adequate rest or proper technique, symptoms may worsen.
Secondary Symptoms
Beyond the primary symptoms, tennis elbow can lead to additional issues that affect quality of life. One common secondary symptom is nighttime discomfort, which can interfere with sleep and overall well-being.
Another secondary symptom is swelling around the elbow joint. This swelling can be a sign of inflammation and may accompany the pain and tenderness.
Stiffness in the elbow, particularly after periods of inactivity, is also possible. This stiffness can make it challenging to perform tasks that require bending or extending the elbow.
These secondary symptoms highlight the importance of addressing tennis elbow promptly. Ignoring these symptoms can prolong recovery and lead to further complications.
Diagnosing Tennis Elbow
Diagnosing tennis elbow typically begins with a physical examination and medical history review. As part of the physical exam, the doctor may apply pressure to the affected area, test grip strength, and assess the patient’s ability to move the elbow, wrist, and fingers. This helps determine the extent of the injury and pinpoint the precise location of the pain.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to rule out other causes of elbow pain. An accurate diagnosis is important in determining the most appropriate treatment path.
Managing and Treating Symptoms
The first line of treatment for tennis elbow is typically non-surgical strategies. Key components of conservative treatment may include:
- Rest to give the affected tendon time to heal
- Physical therapy exercises that strengthen the forearm and reduce strain on the elbow
- Pain relief medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Additional treatment options may include activity modifications to reduce repetitive stress, use of braces or straps to support the elbow. Corticosteroid injections may provide short-term pain relief, but these are used sparingly as it can weaken the tendons around the elbow.
In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical intervention may be considered. The goal is to relieve pain, improve function, and prevent future occurrences of tennis elbow. An experienced elbow specialist can evaluate the injury and help guide the best treatment path for you.
Prevention Tips
To help reduce your risk of developing tennis elbow, consider the following preventive strategies:
- Avoid repetitive wrist and arm motions without breaks
- Apply proper form in sports and physical tasks
- Ensure correct grip size and racket balance for athletes
- Take frequent breaks in activity
- Use ergonomic tools in jobs that involve frequent arm motion
Small adjustments in technique and equipment can help protect your elbow from overuse injuries.
Summary
In summary, tennis elbow is a common condition that can cause significant elbow pain and impact daily activities. Understanding the symptoms, including pain, tenderness, grip strength reduction, and movement-induced pain, is key to early diagnosis and effective treatment.
By following the prevention tips and seeking appropriate treatment options, you can do your part in managing this condition. Taking care of your elbows today can help reduce your risk of increased pain in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes tennis elbow?
Tennis elbow is primarily caused by overuse and repetitive motions that lead to tiny tears and inflammation in the tendons of the outer elbow. Taking breaks and modifying activities can help prevent this condition.
How is tennis elbow diagnosed?
Tennis elbow is diagnosed through a physical examination that evaluates the movement of the elbow, wrist, and fingers, along with measuring grip strength. Imaging tests may be employed if there’s a suspicion of other underlying conditions.
What are the main symptoms of tennis elbow?
The main symptoms of tennis elbow include pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow, reduced grip strength, and pain that worsens with specific arm and wrist movements. It’s important to address these symptoms early to prevent further complications.
What are the treatment options for tennis elbow?
Treatment options for tennis elbow include rest, physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), bracing, corticosteroid injections, and surgery in severe cases. It’s important to consult an elbow specialist to determine the best approach for your individual situation.
How can I prevent tennis elbow?
To reduce your risk of developing tennis elbow, use proper technique during physical activities, take regular breaks, and use ergonomically designed tools or equipment when possible.



